Top 5 Tools for Creating AR Applications

IT copywriter
Reading time:
When it comes to AR applications, developers use AR libraries with open-source API to simplify the development process. Augmented reality is not a new tech trend. Nowadays there are numerous augmented reality tools out there which have similar functions. However, each of the AR frameworks differs from the others by its own specific features.
While working on some of our mobile projects we had an opportunity to try the 5 most popular AR tools in practice. Here is an overview of the selected augmented reality frameworks with their advantages and disadvantages.
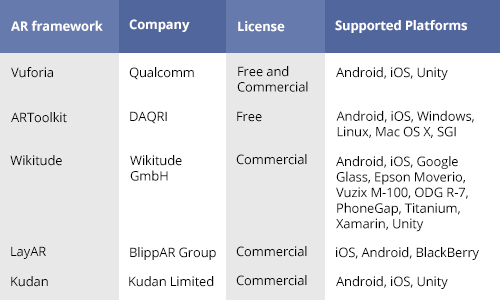
Vuforia
Being a complete SDK for AR applications development, Vuforia supports:
- the detection of several kinds of targets (including objects, images, English text)
- target tracking
- 2D and 3D recognition
- scanning real objects for recognition
- virtual buttons
- mapping additional elements via OpenGL
- Smart TerrainTM, a capability to reconstruct a terrain in real time, creating a 3D geometric map of the environment
- Extended Tracking, a capability that delivers a continuous visual experience even when the target is out of view
In particular, using Vuforia for detecting images, AR applications can appeal to the data that are either local on the device or in the Cloud.
The main advantages of the framework include the support of virtual reality devices and a test app with comments showing the Vuforia abilities.
However, the absence of a complete framework manual leads to complications for the developers working with Vuforia for the first time. Although there are many specific instructions and short tips, they are in random order and cannot replace the required documentation.
The use of cloud recognition has limitations in the free version of Vuforia. Also, a watermark appears in this version once a day.
ARToolKit
ARToolKit is a set of augmented reality software tools that can be used in AR apps. Its main benefit is an open-source code that implies free access to the library.
ARToolKit supports:
- 2D recognition
- mapping additional elements via OpenGL
The library allows tracking known in advance object markers through a mobile device camera and reproducing their location on a device screen. Then a developer can create an app interface using received data.
ARToolKit serves for different platforms: Android, iOS, Windows, Linux, Mac OS X, SGI. Each operating system needs its own development environment. Development environments are free for all the mentioned platforms.
Despite free access to this AR library, the development documentation is quite limited. It includes the test apps, but not all of them can be easily built. The examples are very poor, and there is no information about any plans for the framework update.
Wikitude
Wikitude library supports:
- 2D and 3D recognition
- scanning real objects for recognition
- 3D model rendering and animation
- location tracking
- HTML augmentation
Using Wikitude, developers can create apps to reconstruct places at the virtual map or in the list, to do a search of events, tweets, Wiki articles, or to get the recommendations from other users. Besides a Wikitude-based app allows to receive mobile coupons, information about current specials, and also to play in AR games.
Wikitude can be used for Android and iOS, as a plugin for PhoneGap, a module for Titanium and a component for Xamarin. The Wikitude SDK includes SLAM (markerless tracking) and supports Unity programming language. This framework is available for smart glasses Google Glass, Epson Moverio, Vuzix M-100 and ODG R-7.
There is a free trial version for developers. When you want to use a complete version, be ready for regular payments. As for the documentation, it is well structured and detailed.
LayAR
As follows from the framework name, you can watch the terrain through the layers, that are mapping on the mobile device screen.
LayAR supports:
- image recognition
- mapping additional elements on the base of user location and recognized images
Each of the framework layers could include the data about the location of specific places or social net users. Besides, the LayAR functionality allows considerably expanding the abilities of printed products. For example, using the LayAR-based app, you can make an order in a printed catalog or listen to a song that was mentioned in a magazine.
All the work takes place on a server through JSON, including the logic of mapping additional elements in recognition. For this reason, the work with LayAR is not flexible.
Turning to the benefits, we should say that the documentation is very detailed and well-structured. Although, the framework manual is available only online.
Kudan AR
The Kudan functionality consists of:
- image recognition
- mapping additional elements on the base of user location and recognized images
- markerless tracking (instead of fiducial marks it relies on the use of natural features like the edges, corners, or textures)
- mapping additional elements via separate component over OpenGL
Kudan is faster than other frameworks. This library helps mobile AR apps to map multi-polygonal models in reality and import 3D models from one of the modeling software packages. In addition, the number of recognizing images is not limited and it requires less memory to store files in a device.
Developers can use the basic documentation but the framework manual is short and needs additional information. Also, there is a chance that you can suffer from the limited built-in functionality without a direct access to OpenGL.
In general, the described above augmented reality libraries have a wide range of opportunities for app development from the support of different platforms and to the set of tools for recognizing and tracking objects.
Nevertheless, when it’s time to choose a particular framework, a developer needs to understand what he gets. Some of the tools you can use for free, simply going to the website or downloading the software program. Other tools require signing a contract and paying a fee, but they provide more features with higher quality. Choosing one of the AR tools, think of your project tasks and results you want to achieve, and, after all, match them with the abilities of the AR libraries.

Comments