The Answer to Increased Demand for Cross-Platform Mobile Development

IT copywriter
Reading time:
According to the latest survey by Red Hat, one of the world’s leading software providers, 50% of business today need mobile development specialists. What’s interesting is that among these businesses, native app developers aren’t in high demand. Turns out, front-end web developers and back-end integration specialists take care of a significant portion of mobile development tasks these days.
Moreover, recent Gartner research confirms that businesses are increasingly interested in Cross-Platform mobile development. It is estimated that by the end of 2017 the demand for mobile apps will grow 5 times faster than the staff of software companies that develop these apps.
Trends in Mobile Development
A few years ago, most businesses were betting on native iOS and Android app development, whereas today more companies are considering cross-platform solutions as an alternative. This can be explained by increased demand for rapid development of relatively simple apps.
In fact, many companies need to develop new apps faster than apps can actually be developed. According to Adrian Leow, Principal Research Analyst at Gartner, developing mobile apps quickly and maintaining them is difficult due to a constantly growing demand, rapidly-changing technologies, and a shortage of experienced tech professionals.
50% of businesses today need mobile development specialists.
Generally speaking, there are two types of clients that need mobile app development services:
- The first type needs to develop complex, resource-intensive applications, possibly with unique highly-technical features or multi-layer animations.
- The second type wants relatively simple apps with an adaptive interface, without complicated animation or storage of large volumes of data directly in the mobile device.
It’s not surprising that native app development is a better choice for the first type, while the cross-platform (hybrid) approach is a more reasonable option for the second.
In our practice, we have also been faced with an increased demand for mobile app development. A good part of our clients needs apps with relatively simple functionality, available to users of different mobile platforms. Clients are motivated to compete with other businesses in their niche, so they want to develop apps of tactical rather than strategic nature. In other words, in a highly competitive mobile market, it is increasingly important to be the first to offer the most affordable mobile solution to the user. Following this logic, businesses often prioritize in favor of rapid app development. This is one of the reasons why hybrid development today is no less popular than the native.
PhoneGap Approach to Hybrid Development
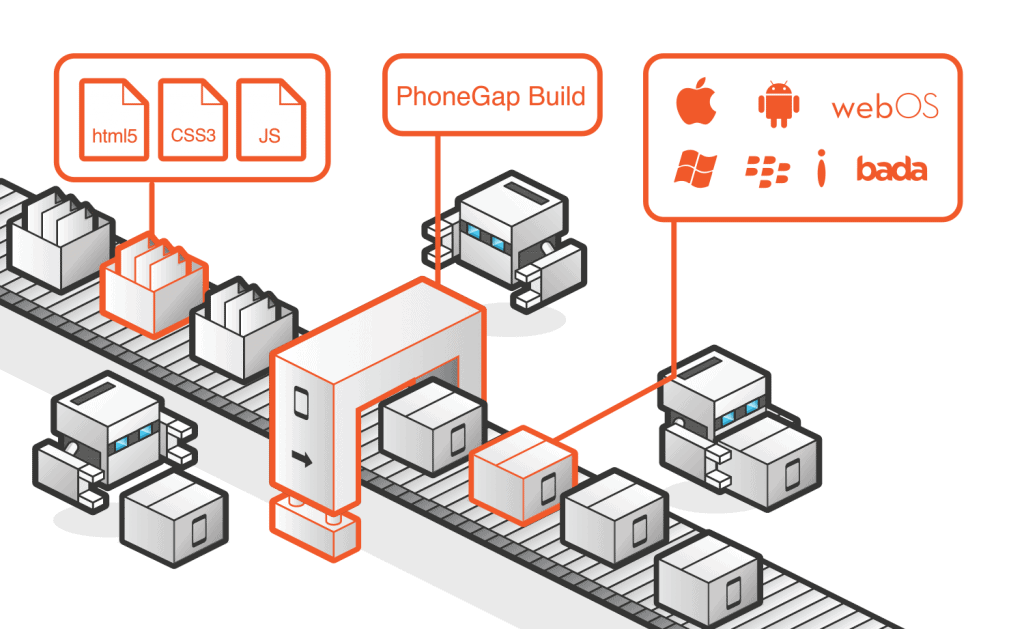
To fully appreciate the hybrid approach, we had to experience it for ourselves. When the number of client requests for mobile development has grown dramatically and all our mobile developers had their hands full, we turned to our web development team for help. We carefully studied various technical tools available out there and eventually decided to use PhoneGap for developing hybrid apps.
PhoneGap is an open framework that helps speed-up the development of cross-platform applications. PhoneGap makes it possible to write apps using HTML5 + JavaScript, and then compile them into installation files for any operating system (iOS, Android, Windows Phone, BlackBerry).
In short, the whole point of hybrid development is that we can work with WebView of the mobile phone using HTML5/Javascript/CSS, and then simply ‘package’ the resulting solution into a native ‘wrapper’.
Thanks to PhoneGap we can:
- Create mobile versions of a websites with responsive design;
- Achieve full interaction with all features of the mobile device, made possible by PhoneGap plug-ins written in native programming language and offering public methods of JavaScript;
- Offer the option of integrating the app with any mobile platform.
Most mobile users won’t ever notice the difference between hybrid and native apps.
Essentially, PhoneGap lets us create mobile apps using web technologies. Most mobile users won’t ever notice the difference, since such an app is downloaded on the mobile device and looks just like a native app. This being said, the difference does exist and should be taken into account when choosing between native and hybrid app development.
Pros and Cons of Hybrid App Development

Generally speaking, the main advantages of the hybrid approach include:
- Cross-platform: having developed one app, you can then apply it to any operating system (iOS, Android, Windows Phone, BlackBerry);
- Affordable development costs: much lower than developing a native app;
- Using the same language (JavaScript);
- Access to the main data of the mobile device: GPS, camera, contacts, etc. The app works in offline mode;
- The ability to distribute the app through official app stores.
In fact, hybrid development is a popular approach among many world-famous companies. Just to name a few well-known apps that are cross-platform: Wikipedia, HealthTap, BBC Sport App, Evernote, and more. Users have downloaded these applications over a million times, which indicates the high quality and popularity of these solutions.
A few well-known cross-platform apps: Wikipedia, HealthTap, BBC Sport App, Evernote, and more.
However, hybrid development approach also has some weaknesses:
- Reduced speed as compared to native applications;
- Limited access to device data;
- Challenges with responsive design layout. Even though there are lots of various web frameworks available for building mobile apps, we were faced with the problem that they all behave differently on different devices;
- Appearance of bugs that may interfere with normal functioning of app. Fixing different bugs on different operating systems has led to new bugs down the road, as mobile operating systems are frequently updated;
- Limited representation of visual and graphic elements, such as animations.
Although some of these shortcomings aren’t too critical, the low productivity and problems with animations may become deal-beakers for some cross-platform applications. For example, Facebook and LinkedIn mobile apps were at one point cross-platform, but were later rewritten as native apps. According to both Facebook and LinkedIn developers, they saw a two-fold increase in productivity when they switched to native apps.
To summarize, you should consider the hybrid approach if:
- Your goal is to rapidly develop apps for more than 2 mobile platforms;
- You have a limited budget;
- You need a relatively simple app without complex animations;
- You can exclude support for many parameters of native functionality.
Bottom line is, we can confidently say that global trends in mobile development are confirmed by our own experience — the demand for mobile apps, the speed of mobile development, the demand for simple apps with affordable development costs are all on the rise. All this opens up opportunities for improving hybrid applications, which in many cases are just as good as native apps. When choosing one or the other, it is important to monitor the market and to set priorities concerning development time-frame, cost, and performance requirements.

Comments